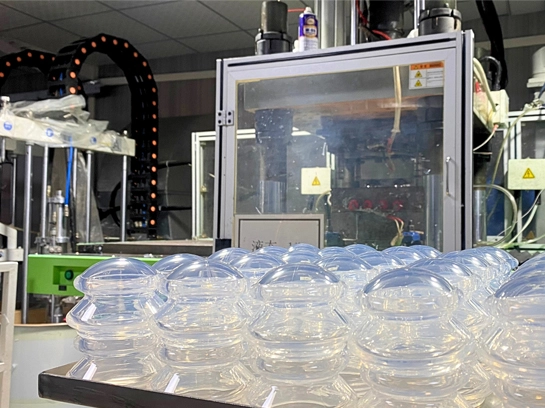
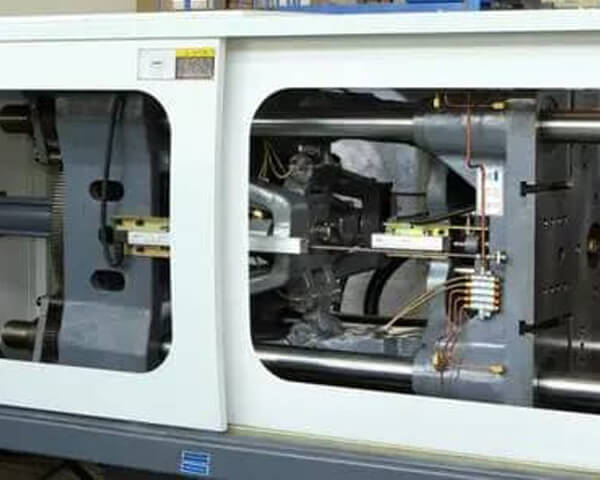
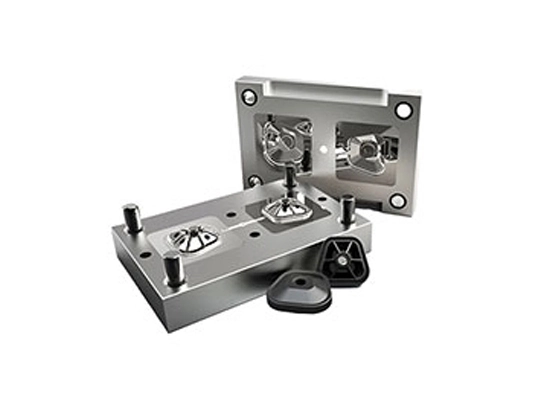
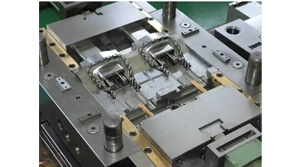
Compression molding is a manufacturing process that involves placing a pre-measured quantity of material (usually a polymer, rubber, or composite) into a heated mold cavity. The material is then compressed under high pressure, causing it to flow and conform to the shape of the mold. Once the material solidifies, the part is ejected from the mold.
This method is particularly effective for creating complex, durable parts with consistent quality. Compression molding is known for its ability to handle high-strength materials, making it ideal for demanding applications in industries like electrical, automotive, and consumer products.
Compression molding is used in a wide range of industries due to its versatility and ability to produce strong, durable parts. Some common applications include:
1. Automotive Components
· Gaskets, seals, and bumpers.
· Lightweight and durable interior and exterior parts.
2. Consumer Products
· Handles and housing for food and medical products.
· Sports equipment and household items made from durable polymers.
3. Electrical and Electronic Components
· Insulators, connectors, and switches.
· Heat-resistant parts for high-voltage applications.
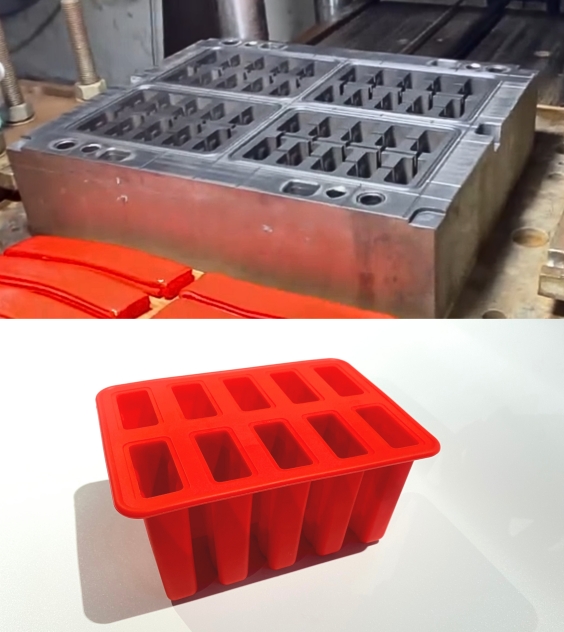

Compression molding supports a wide range of materials, making it suitable for diverse applications. Some commonly used materials include:
Thermosetting Plastics: Epoxy, phenolic, and melamine resins for high-strength parts.
Rubber: Natural and synthetic rubber for seals, gaskets, and shock-absorbing components.
Composites: Glass-filled or carbon-filled materials for lightweight, high-performance parts.
Elastomers: Flexible materials for parts that require elasticity and durability.
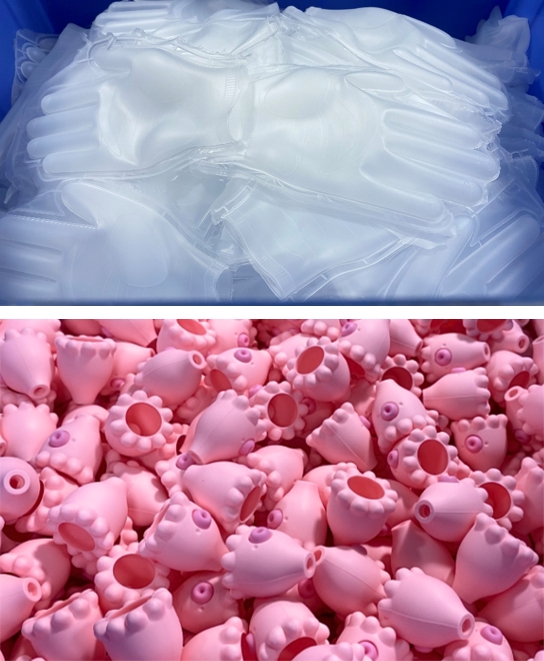


_20250123.webp)